How to Increade Linear Feed Rate Milling
This page introduces formulas for calculating basic parameters necessary for face milling. The figures obtained from the calculation are for reference only. The conditions for machining depend on the machine tool you are using. Use the optimal conditions according to your actual machining circumstances.
- Cutting Speed (vc)
- Feed per Tooth (f)
- Table Feed (Vf)
- Machining Time (Tc)
- Net Power (Pc)
- Kc Values
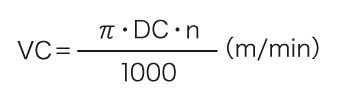
- π (3.14): Circular constant
- DC (mm): Cutter diameter
- n (min-1): Spindle speed
- memo
-
This formula is used to calculate the cutting speed from the spindle speed and the outer diameter of the cutter.
Example:
Cutter diameter (DC) = 100 mm
Spindle speed (n) = 400 min-1
In this case, the cutting speed (vc) is approximately 125.6 m/min.
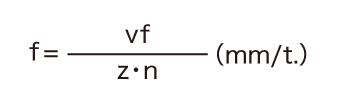
- vf (mm/min): Table feed per minute
- z: Number of teeth
- n (min-1): Spindle speed (Feed rate fr = zxfz)
- memo
-
This formula is used to calculate the feed per tooth from the table feed per minute (feed rate), the number of teeth, and the spindle speed.
Example:
Table feed per minute (vf) = 450 mm/min
Number of teeth (z) = 10
Spindle speed (n) = 600 min-1
In this case, the feed per tooth (f) is 0.075 mm/t.
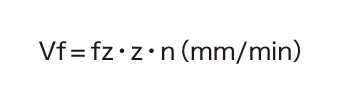
- fz (mm/tooth): Feed per tooth
- z: Number of teeth
- n (min-1): Spindle speed (Feed rate fr = zxfz)
- memo
-
This formula is used to calculate the table feed per minute (feed rate) from the feed per tooth, the number of teeth, and the spindle speed.
Example:
Feed per tooth (fz) = 0.2 mm/tooth
Number of teeth (z) = 8
Spindle speed (n) = 600 min-1
In this case, the table feed rate is 960 mm/min.
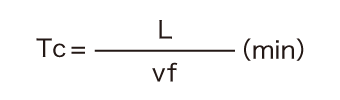
- L (mm): Total table feed length (Length of material (l) + Face mill diameter (DC))
- vf (mm/min): Table feed per minute
- memo
-
This formula is used to calculate the machining time from the total table feed length and the table feed per minute (feed rate).
Example of finishing a block of FC200 cast iron to have a flat surface of:
Width = 150 m
Length = 250 mm
Face milling conditions used:
Feed per tooth (fz) = 0.35 mm
Number of teeth (z) = 12
Spindle speed (n) = 200 min-1
Cutting speed (vc) = 120 m/min
Face mill diameter (D1) = 220 mm
In this case,
the table feed per minute (vf) and the total table feed length (L) are:
vf = 0.35 × 12 × 200 = 840 mm/min
L = 350 + 220 = 570 mm
Substitute these values into the formula:
Tc = L ÷ vf
= 570 ÷ 1120
= 0.679 (min) × 60
= 40.74 (sec)
The machining time (Tc) is approximately 40.74 seconds.
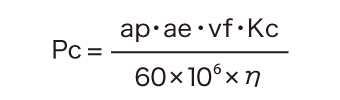
- ap (mm): Depth of cut
- ae (mm): Width of cut
- vf (mm/min): Table feed per minute
- Kc (MPa): Specific cutting force
- η: Machine efficiency
- memo
-
This formula is used to calculate the net power required for face milling based on the depth and width of cut, the table feed per minute, the specific cutting force, and the machine efficiency. Example of calculating the net power required to cut tool steel with:
Depth of cut (ap) = 5 mm
Width of cut (ae) = 70 mm
Table feed per minute (vf) = 300 mm/min
Other conditions:
Specific cutting force (Kc) = 1800 MPa
Machine efficiency (η) = 80% (0.8)
Cutting speed (vc) = 80 m/min
Cutter diameter (DC) = 250 mm
Number of teeth (z) = 16
In this case, first you calculate the spindle speed (n) and then the feed per tooth of the cutter (fz).
Spindle speed (n) = 1000・vc ÷ π・D
= (1000 × 80) ÷ (3.14 × 250)
= 101.91 min-1
Feed per tooth (fz) = vf ÷ (Z × n)
= 300 ÷ (16 × 101.91)
= 0.184 mm/tooth
Substitute the above into the formula:
Pc = (5 × 70 × 300 × 1800) ÷ (60 × 106× 0.8)
= 3.937 kw
The net power required for face milling (Pc) is approximately 3.94 kW.
| Workpiece material | Tensile strength (MPa) and stiffness | Specific cutting force Kc (MPa) for each feed | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 (mm/tooth) | 0.2 (mm/tooth) | 0.3 (mm/tooth) | 0.4 (mm/tooth) | 0.6 (mm/tooth) | ||
| Mild steel (SS400, S10C, etc.) | 520 | 2200 | 1950 | 1820 | 1700 | 1580 |
| Medium steel (S45C, S50C, etc.) | 620 | 1980 | 1800 | 1730 | 1600 | 1570 |
| Hard steel (S55C, S58C, etc.) | 720 | 2520 | 2200 | 2040 | 1850 | 1740 |
| Tool steel (Carbon tool steel (SK), etc.) | 670 | 1980 | 1800 | 1730 | 1700 | 1600 |
| Tool steel (Alloy tool steel (SKS), etc.) | 770 | 2030 | 1800 | 1750 | 1700 | 1580 |
| Chrome-manganese steel (Manganese carbide (MnC), etc.) | 770 | 2300 | 2000 | 1880 | 1750 | 1660 |
| Chrome-manganese steel (Manganese carbide (MnC), etc.) | 630 | 2750 | 2300 | 2060 | 1800 | 1780 |
| Chrome molybdenum steel (SCM grades, etc.) | 730 | 2540 | 2250 | 2140 | 2000 | 1800 |
| Chrome molybdenum steel (SCM grades, etc.) | 600 | 2180 | 2000 | 1860 | 1800 | 1670 |
| Nickel chrome molybdenum steel (SNCM415, etc.) | 940 | 2000 | 1800 | 1680 | 1600 | 1500 |
| Nickel chrome molybdenum steel (SNCM439, etc.) | 352HB | 2100 | 1900 | 1760 | 1700 | 1530 |
| Austenitic stainless steel (SUS304, etc.) | 155HB | 2030 | 1970 | 1900 | 1770 | 1710 |
| Cast steel (SCC, etc.) | 520 | 2800 | 2500 | 2320 | 2200 | 2040 |
| Hard cast iron | 46HRC | 3000 | 2700 | 2500 | 2400 | 2200 |
| Meehanite cast iron (FC350, etc.) | 360 | 2180 | 2000 | 1750 | 1600 | 1470 |
| Gray cast iron (FC250, etc.) | 200HB | 1750 | 1400 | 1240 | 1050 | 970 |
| Brass (C3710, etc.) | 500 | 1150 | 950 | 800 | 700 | 630 |
| Light alloy (Al-Mg, A5005, etc.) | 160 | 580 | 480 | 400 | 350 | 320 |
| Light alloy (Al-Si, A4032, etc.) | 200 | 700 | 600 | 490 | 450 | 390 |
| Light alloy (Al-Zn-Mg-Cu, A7075, etc.) | 570 | 880 | 840 | 840 | 810 | 720 |
INDEX
torresauntrunt1959.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.keyence.com/ss/products/measure-sys/machining/formula/milling.jsp
0 Response to "How to Increade Linear Feed Rate Milling"
Post a Comment